A previous entry (http://sas-and-r.blogspot.com/2017/07/options-for-teaching-r-to-beginners.html) describes an approach to teaching graphics in R that also “get[s] students doing powerful things quickly”, as David Robinson suggested.
In this guest blog entry, Randall Pruim offers an alternative way based on a different formula interface. Here’s Randall:
For a number of years I and several of my colleagues have been teaching R to beginners using an approach that includes a combination of
- the
latticepackage for graphics, - several functions from the
statspackage for modeling (e.g.,lm(), t.test()), and - the
mosaicpackage for numerical summaries and for smoothing over edge cases and inconsistencies in the other two components.
Important in this approach is the syntactic similarity that the following “formula template” brings to all of these operations.
goal ( y ~ x , data = mydata, … )
Trouble in paradise
As the earlier post noted, the use of
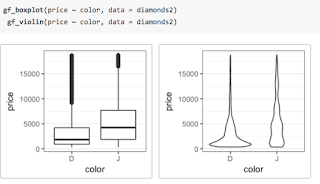
lattice has some drawbacks. While basic graphs like histograms, boxplots, scatterplots, and quantile-quantile plots are simple to make with lattice, it is challenging to combine these simple plots into more complex plots or to plot data from multiple data sources. Splitting data into subgroups and either overlaying with multiple colors or separating into sub-plots (facets) is easy, but the labeling of such plots is not as convenient (and takes more space) than the equivalent plots made with ggplot2. And in our experience, students generally find the look of ggplot2 graphics more appealing.
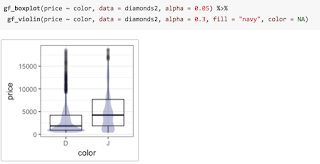
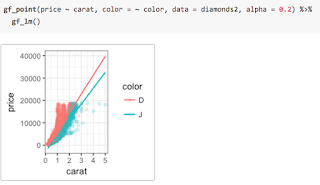
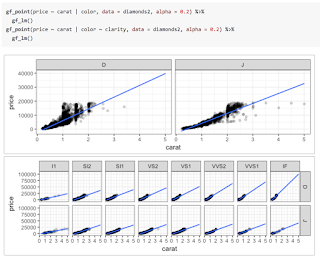
ggplot2 into a first course is challenging. The syntax tends to be more verbose, so it takes up more of the limited space on projected images and course handouts. More importantly, the syntax is entirely unrelated to the syntax used for other aspects of the course. For those adopting a “Less Volume, More Creativity” approach, ggplot2 is tough to justify.ggformula, an R package that provides a formula interface to ggplot2 graphics. Our hope is that this provides the best aspects of lattice (the formula interface and lighter syntax) and ggplot2 (modularity, layering, and better visual aesthetics).gf. Here are two examples, either of which could replace the side-by-side boxplots made with lattice in the previous post.%>%, also commonly called a pipe) between the two layers and adjust the transparency so we can see both where they overlap.ggformula package provides two ways to create these facets. The first uses | very much like lattice does. Notice that the gf_lm() layer inherits information from the the gf_points() layer in these plots, saving some typing when the information is the same in multiple layers.gf_facet_wrap() or gf_facet_grid() and can be more convenient for complex plots or when customization of facets is desired.ggformala also fits into a tidyverse-style workflow (arguably better than ggplot2 itself does). Data can be piped into the initial call to a ggformula function and there is no need to switch between %>% and + when moving from data transformations to plot operations.ggformula strengthens this approach by bringing a richer graphical system into reach for beginners without introducing new syntactical structures. The full range of ggplot2 features and customizations remains available, and the ggformula package vignettes and tutorials describe these in more detail.— Randall Pruim